what neuron runs from the cns to the autonomic ganglion
Introduction [edit | edit source]
A ganglion is a collection of neuronal bodies found in the voluntary and autonomic branches of the peripheral nervous organization (PNS).
Ganglia tin can be thought of as synaptic relay stations between neurons. The information enters the ganglia, excites the neuron in the ganglia and so exits[1].
Among vertebrate animals there are three major groups of ganglia. These include:
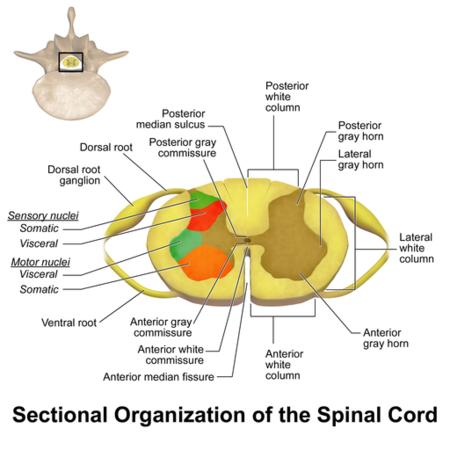
- Dorsal root ganglia or spinal ganglia where the cell bodies of sensory or afferent fretfulness are located See Image ane
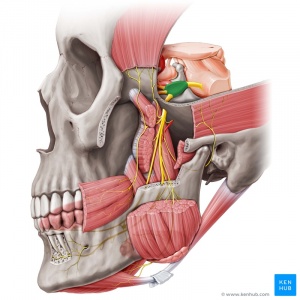
- Cranial nerve ganglia that contain the neurons of the selected cranial nervesRun across paradigm ii Trigeminal ganglion highlighted in greenish.
- Autonomic ganglia, which comprise the cell bodies of the autonomic nervous system. See epitome iii
Image 1: Shows the Autonomic Ganglia (blood-red SNS, bluish PNS)
In addition to the ganglion of the peripheral nervous arrangement, at that place are also parts of the brain that contains a cluster of interconnected nuceli chosen the basal ganglia[ii]
Structure [edit | edit source]
Ganglia are oval in structure and contain
- Neuronal cell bodies (somata)
- Satellite glial cells, environment neurons in the sensory, sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia and aid regulate the chemical environment. They may contribute to chronic pain.[3]
- A dense connective tissue sheathing covers the ganglion, with a single layer of flat shaped satellite cells surrounding each neuronal jail cell body.
- A basement membrane covers the outer region of the satellite cells.
Iii Major Groups Of Ganglia [edit | edit source]
- A spinal ganglion (dorsal root ganglion) is a cluster of nerve bodies positioned along the spinal cord at the dorsal and ventral roots of a spinal nerve. The dorsal root ganglia contain the prison cell bodies of afferent nerve fibres (those conveying impulses toward the cardinal nervous organization); efferent neurons (carrying motor impulses abroad from the central nervous organisation) are present in the ventral root ganglia.See prototype 1.
- Cranial Nerve Ganglion (not all CN have) is analogous to the dorsal root ganglion, except that it is associated with a cranial nerve, instead of a spinal nerve (associated with the spinal cord). The roots of cranial nerves are within the skull, whereas the ganglia are exterior the skull. Eg, The vagus nerve has 2 sensory ganglia, the superior and the inferior ganglia both outside the skull; the trigeminal ganglion is exterior to the temporal bone . Like the sensory neurons associated with the spinal cord, the sensory neurons of cranial nerve ganglia are unipolar in shape with associated satellite glial cells[4].
-
At that place are ii types of Autonomic Ganglia: the sympathetic and the parasympathetic based on their functions. The former tend to be located shut to the spinal cord whereas the later lie near or within the viscera of the peripheral organs that they innervate.[4]. See image three Shows the Autonomic Ganglia (red SNS, blue PNS).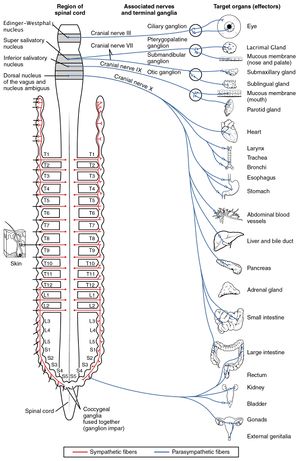
Sensory ganglia [edit | edit source]
The cell bodies of somatic sensory and visceral sensory neurons are institute in the dorsal root ganglia of spinal fretfulness, and on the ganglia of selected cranial nerves. Hence known equally sensory ganglia.
i.Dorsal root ganglia:
- most common blazon of sensory ganglia. They are found in the posterior (dorsal) root of spinal nerves, following the emergence of the dorsal root, that emerges from the intervertebral neural foramina
- contain clusters of sensory neuron cell bodies which transmit messages relating to hurting, bear upon, and temperature from the PNS, towards the CNS. Satellite glial cells separate and inhibit interaction between jail cell bodies in the ganglion.
- Near of the body's sensory neurons are contained here.

2. Sensory ganglia of the cranial nerves
Another type of sensory ganglia, are the ones that are found in the cranial nerves. Those are ganglia with special sensory functions and they are similar to the dorsal root ganglia except for they are associated with the cranial nerves and not the spinal nerves[one].
Primal Facts [edit | edit source]
Ganglion: Collection of neuron cell bodies located in the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Types:
- Sensory ganglia: Dorsal root ganglia of spinal nerves and the ganglia of selected cranial nerves.
- Autonomic ganglia: Sympathetic (shut to the spinal cord), Parasympathetic (virtually on in the viscera)[1].
Trivia Fact [edit | edit source]

With invertebrates, ganglia ofttimes do the piece of work of a brain.
- Eg The earthworm has a ganglion above the gut at the forepart. This is linked to another nether the gut by nerve fibres running down each side of the gut. The residual of the fundamental nervous system runs under the gut. This type of arrangement in found in a number of invertebrate phyla, and contrasts with the vertebrates, who have their spinal cord higher up (dorsal to) their gut[five].
The brain and the spinal cord are the primary organs of the central nervous organization.The nerves and ganglia are the primary components of the peripheral nervous system.[six]
References [edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 ken Hub Ganglion Available from:https://world wide web.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/nerve-ganglia (accessed v.2.2021)
- ↑ New Medical Ganglion Available from:https://www.news-medical.internet/wellness/What-is-a-Ganglion.aspx (accessed 5.2.2021)
- ↑ QBI glial cells Bachelor from:https://qbi.uq.edu.au/brain-basics/brain/encephalon-physiology/types-glia (accessed vi.two.2021)
- ↑ 4.0 4.one OSE Ganglia and nerves Available from:https://open up.oregonstate.instruction/aandp/chapter/xiii-ii-ganglia-and-nerves/ (accessed 5.two.2021)
- ↑ Kidzsearch Ganglionhttps://wiki.kidzsearch.com/wiki/Ganglion (accessed 6.2.2021)
- ↑ Facts for Kids nervous System Available from: https://www.factsjustforkids.com/human being-body-facts/nervous-system-facts-for-kids.html (accessed 6.two.2021)
bergspectlemeded1971.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.physio-pedia.com/Ganglion
0 Response to "what neuron runs from the cns to the autonomic ganglion"
Post a Comment